
Causes of Urinary Burning Sensation
Causes of Urinary Burning Sensation
Dysuria (painful urination) is a catch-all term for any type of urinary discomfort. This discomfort can originate in the bladder, urethra, or perineum.
The urethra is the tube that transports urine from your body to the outside world. In those who have a penis, the perineum is the area between the scrotum/vagina and the anus.
Urination that causes pain is fairly common in today's society. A variety of medical conditions can cause pain, burning, or stinging. Let us go over the causes in detail.
What makes urinating painful?
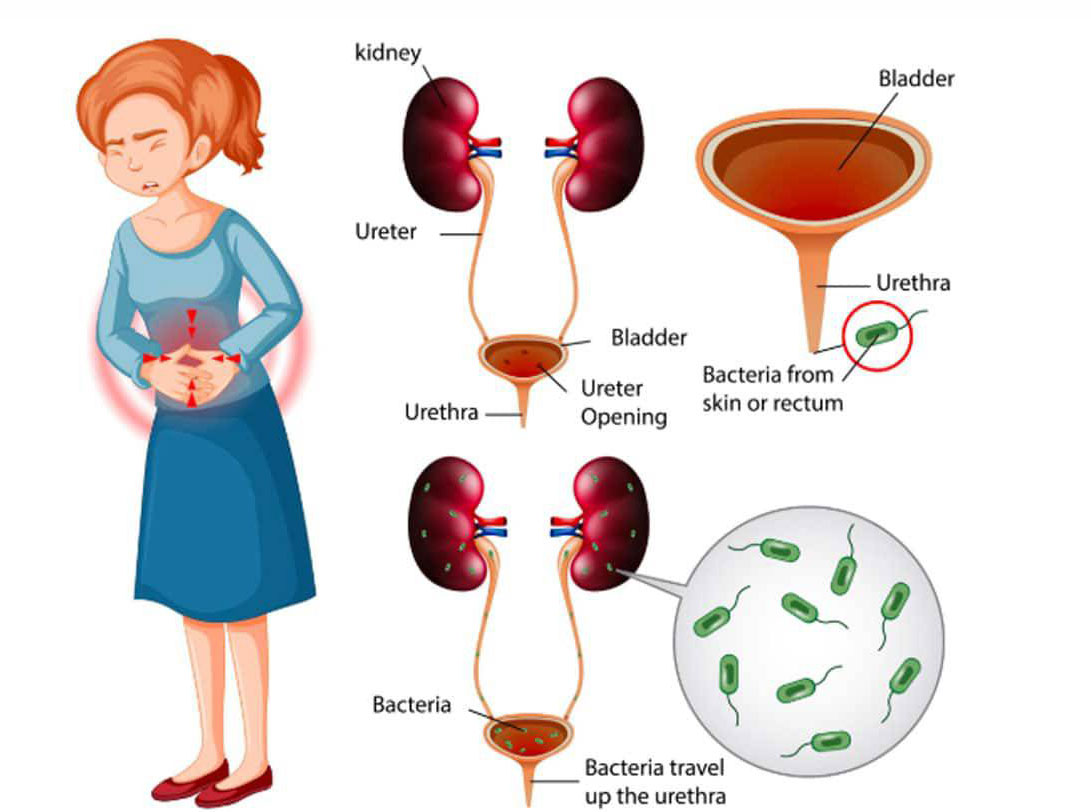
UTIs (urinary tract infections)
Urination that causes pain is a common sign of a urinary tract infection (UTI). A bacterial infection can cause a urinary tract infection. Inflammation of the urinary tract could also be to blame.
The urinary tract is made up of the urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidneys. The ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Inflammation in any of these organs can cause urinary pain.
People with a vaginal canal are more likely to develop UTIs than those with a penis. This is due to the fact that those who have a vagina have a shorter urethra. When the urethra is shorter, bacteria must travel a shorter distance to enter the bladder.
Furthermore, urinary tract infections are more common in pregnant women and menopausal women.
Prostatitis
Urinary pain can be caused by a number of medical conditions. Prostatitis can cause painful urination in men with prostate disease. This syndrome causes inflammation of the prostate gland. It becomes a common cause of urinary tract burning, stinging, and pain.
Urethritis
Urethritis is a condition in which the urethra becomes inflamed, usually as a result of a bacterial infection. Urinary pain and an increased desire to pee are symptoms of urethritis.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
The fallopian tubes, ovaries, cervix, and uterus are all affected by PID. Among the symptoms are abdominal pain, uncomfortable intercourse, and painful urine.
PID is a potentially fatal condition caused by a bacterial infection that begins in the cervix and spreads to the reproductive organs.
Cystitis
Cystitis, or inflammation of the bladder lining, is another cause of painful urination. Painful bladder syndrome is another name for interstitial cystitis (IC). This is the most common type of cystitis. IC symptoms include bladder and pelvic pain and discomfort.
Radiation therapy may cause bladder and urine pain in some people, resulting in Radiation cystitis.
Uropathy with obstruction
Obstructive uropathy occurs when the ureter, bladder, or urethra become obstructed, causing urine to flow back into the kidneys. Despite the fact that the causes vary, it is critical to seek medical attention as soon as symptoms appear.
Another condition, urethral stricture, causes a constriction of the urethra, causing similar urination and discomfort issues.
Kidney stone disease
Kidney stones are solidified masses of material in the urinary tract. If you have kidney stones, it may be difficult to urinate comfortably.
Medications
Several drugs, including cancer treatments and antibiotics, can cause painful urination as a side effect. Any side effects from your medications should be discussed with your doctor.
Supplies for personal hygiene
Infection does not always cause painful urination. It can also be caused by the products you use in your genital area. Vaginal tissues can be irritated by soaps, lotions, and bubble baths, in particular.
Dyes found in laundry detergents and other toiletries can cause skin irritation and painful urination.
What are the options for treating painful urination?
The first step in treating pain is determining what is causing it. Your doctor may prescribe medication to treat painful urination. Antibiotics are effective in treating urinary tract infections, bacterial infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. In addition, your doctor may prescribe medication to help you deal with your inflamed bladder.
When you begin taking antibiotics for a bacterial infection, your painful urinating usually improves quickly. Always follow your doctor's instructions when taking medication. Some infections, such as interstitial cystitis, cause more difficult-to-manage pain. Pharmacological therapy may take longer to take effect. It may take up to four months of medication before you feel better. It can, however, be treated with a proper routine and medications.
Conclusion
Dysuria, which causes pain, discomfort, and/or a burning sensation, is a symptom of the disease. Because this ailment is bothersome, you will most likely need to contact your doctor. Consult your doctor to determine whether your symptom is caused by a urinary tract infection or something else.
In any case, the sooner you see the best urologists in Hyderabad, the sooner you will be able to receive a diagnosis and begin treatment.
0 comments