
Everything You Need to Know About Micro Laparoscopic Gastrointestinal Surgery
Everything You Need to Know About Micro Laparoscopic Gastrointestinal Surgery
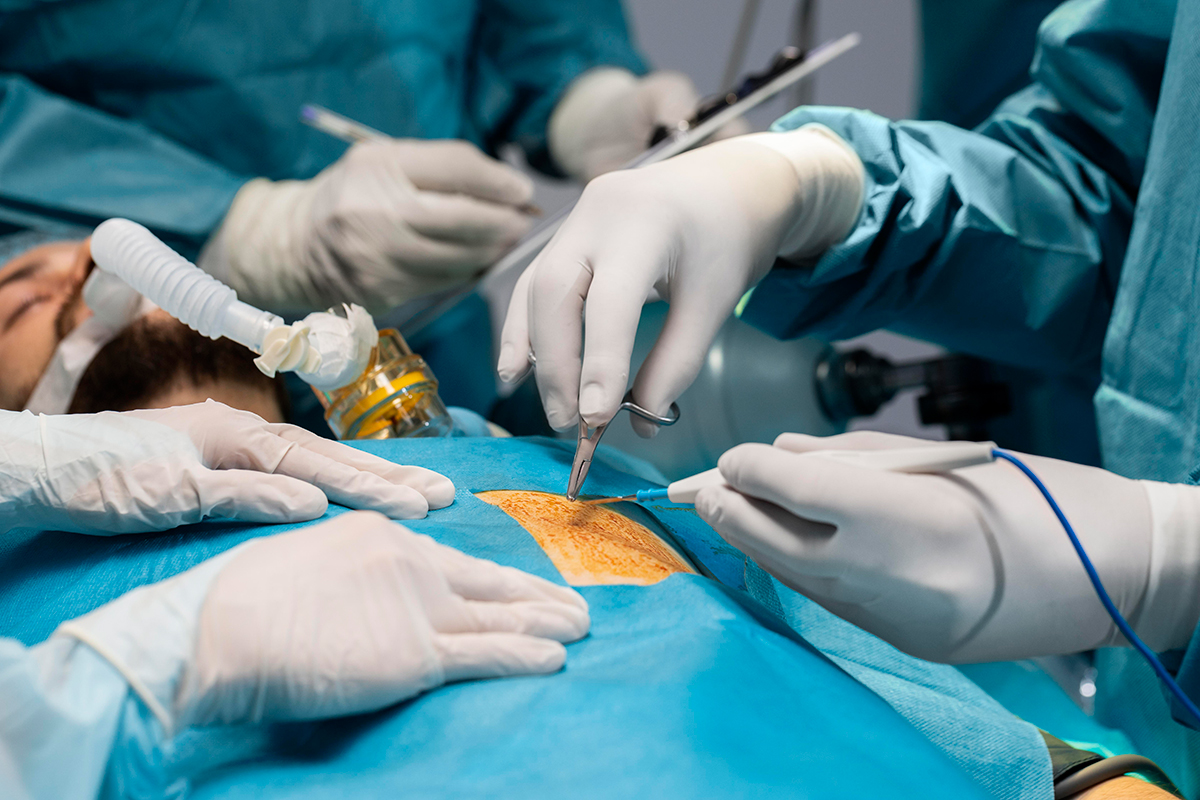
Although the micro-laparoscopic platform requires a smaller incision than conventional laparoscopic surgery, it still enables the use of fully functional standard laparoscopic instruments, which may lead to less scarring, less pain, an earlier return to normalcy, and good cosmetic results.
Small incisions are a benefit of using the same 3-mm instruments as in standard laparoscopy. Using the percutaneous system requires only minor adjustments to surgeons' procedures, aside from the smaller incisions.
Laparoscopic surgery has been the gold standard for treating a variety of surgical conditions since it was introduced in the late 1980s. This is because it offers advantages like post-operative recovery, an earlier return to work, little pain, few wound complications, and stunning cosmesis. One of the biggest revolutions in surgical innovation in history, according to many.
In recent years, surgeons have worked to enhance laparoscopic surgery methods. Microlaparoscopy is one such advancement. In its early stages, laparoscopic surgery employed instruments with a 10mm diameter. The size decreased over time and as the field developed, falling between 3 and 5mm.
How is the process carried out?
The term "laparoscopy," which is also used to refer to minimally invasive surgery, comes from the name of a thin instrument called a "laparoscope" that has a tiny camera and light on the end and allows medical professionals to see inside the body through a small incision rather than a large one.
Three or more small (5-10 mm) abdominal incisions are needed for laparoscopic surgery in order to place access ports. The procedure can then continue after the surgeon passes the laparoscope and surgical tools through these ports to get a visual of the abdominal organs on a video monitor.
How should I get ready for a laparoscopic procedure? A general physical examination will be performed after the patient has been asked to give blood samples, answer questions regarding their medical history, have a chest X-ray, and undergo lung function tests. The night before surgery, the patient must then take a laxative and clear their intestines.
The patient will then meet with an anesthesiologist to discuss the kind of painkillers that will be administered throughout the procedure. To lessen the chance of contracting an infection from bacteria that are naturally present in the intestine, it is advised to carefully follow the directions and consume all of the laxatives.
Weight loss and bariatric surgery
Gastric bypass after a sleeve gastrectomy
Re-do GI procedures
Following bariatric surgery, weight gain.
Bile duct injuries treated with biliary enteric surgery.
Laparoscopic Colorectal Operations
Abdominoperineal Resection: In patients with cancer of the anus or lower part of the rectum, abdominal resection is used to remove the rectum, anus, and sigmoid colon. In order to remove waste and feces from the body, the surgeon removes the rectum and anus and makes a colostomy (an arrangement to connect the healthy end of the colon to the anterior wall of the abdomen through an incision)..
Diverticulitis, an infection or inflammation of the diverticula, and polyps—both cancerous and non-cancerous growths—can both call for a proctosigmoidectomy, which involves removing the affected portion of the sigmoid colon or the rectum..
Total abdominal colectomy: Laparoscopic surgery is used to treat Crohn’s disease (an inflammatory bowel disease that causes abdominal pain and a variety of other symptoms), Ulcerative colitis (severe colon inflammation), and Familial polyposis (a condition that causes the formation of numerous colon polyps), followed by surgical removal of the large intestine during a total abdominal colectomy.
The right side of the colon or large intestine is surgically removed during a right colectomy, also referred to as an ileocolectomy. The small intestine's end is also removed during the excision. (attached to the right side of the colon). The right colectomy is used to treat polyps, cancer, and the signs of Crohn's disease.
Rectopexy: When the rectum protrudes from its normal position due to rectal prolapse, a rectopexy can help sew the rectum back into place..
Total proctocolectomy: This laparoscopic procedure removes the large intestine, the rectum, and the anus, and is extremely beneficial for people with Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. The surgery may be followed by a transient ileostomy to remove wastes from the body.
How safe is laparoscopy? When should you consult after a laparoscopy?
The procedure of a laparoscopy is very safe. But as soon as you notice any of the following signs, call your doctor right away:.
more than 24 hours of vomiting and nausea.
100+ degree Fahrenheit temperatures for more than 24 hours..
Around your wound, there may be redness, swelling, soreness, drainage, or bleeding..
breathing issues or shortness of breath.
Heavy menstrual flow, heavy bleeding with clots, or soaking in a sanitary pad in less than two hours after the first day of surgery. .
The majority of the time, patients can go back home soon after their laparoscopy. You need to hold off until your anesthesia wears off and your doctor is sure you aren't suffering any negative effects from the procedure.

0 comments