
How Mumps causes and Its Symptoms
How Mumps causes and Its Symptoms
Mumps is a viral infection that is caused by the mumps virus. The virus is primarily spread through respiratory secretions, such as saliva or mucus, from an infected person.
When an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes, tiny droplets of saliva or mucus containing the virus can be spread into the air. If another person inhales these droplets, they can become infected with the mumps virus.
Mumps can also be spread through direct contact with an infected person's saliva or mucus. This can happen when a person touches an object that has been contaminated with the virus and then touches their mouth or nose.
The mumps virus can be particularly contagious, with up to 90% of people who come into close contact with an infected person becoming infected themselves if they are not immune.
The best way to prevent mumps is to get vaccinated with the MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine. This vaccine is highly effective in preventing mumps and is recommended for all children, as well as for adults who have not been vaccinated or have not had the disease before.
Symptoms:
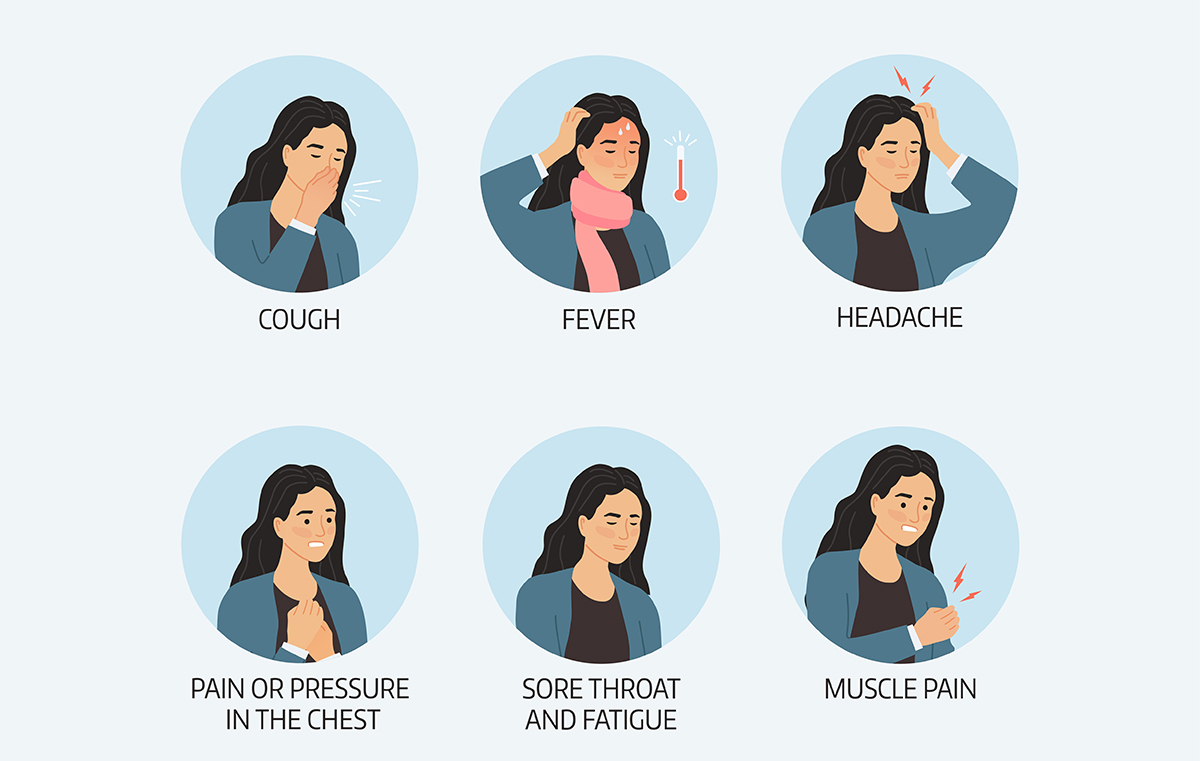
The symptoms of mumps typically develop 2-3 weeks after a person is infected with the virus. The most common symptoms of mumps include:
1.Swelling of the salivary glands: The hallmark symptom of mumps is the swelling of one or both parotid glands, which are located just below the ears. The swelling can be mild or severe, and it can cause pain and tenderness in the affected area.
2.Fever: A fever is a common symptom of mumps and can range from mild to high.
3.Headache: Many people with mumps also experience headaches, which can range from mild to severe.
4.Muscle aches: Muscle aches are another common symptom of mumps, and they can affect various parts of the body.
5.Fatigue: Many people with mumps feel very tired and lack energy.
6.Loss of appetite: Some people with mumps may experience a loss of appetite, which can lead to weight loss.
In rare cases, mumps can lead to more serious complications, such as meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain and spinal cord), encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), or orchitis (inflammation of the testicles). If you suspect that you or someone you know has mumps, it is important to seek medical attention.

0 comments