
What exactly is liver inflammation? What Causes It and How to Treat It
What exactly is liver inflammation? What Causes It and How to Treat It
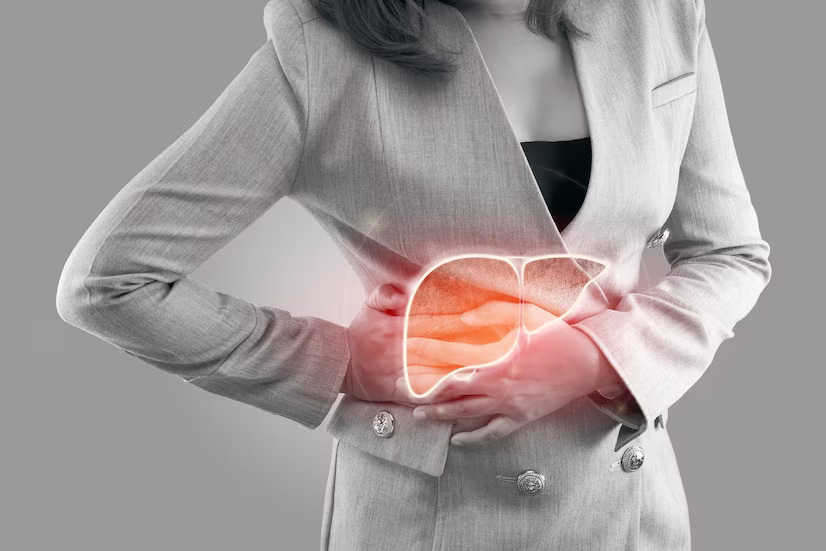
What exactly is liver inflammation?
The liver is one of the digestive system's organs. It is involved in the removal of toxins from your blood as well as the production of bile and certain hormones. It regulates fat storage and synthesis in your body, as well as cholesterol secretion. These functions cannot be carried out properly when the liver is inflamed.
Inflammation is the body's natural response to anything foreign that enters it. This indicates that white blood cells are being sent to combat the invader. Every day, the body is exposed to various toxins such as alcohol, fatty foods, and prescription and non-prescription drugs.
Liver inflammation disease occurs when the liver's cells are damaged. Hepatitis is the medical term for this condition. The most common type of liver inflammation is viral hepatitis.
Fatigue, jaundice (general yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes), feeling satiated immediately after a meal, nausea or vomiting sensations, and severe abdominal pain are all symptoms of an inflamed liver.
Types of Liver Inflammation
The most common cause of liver inflammation is viral infection. Hepatitis viruses can be classified into five types:
Hepatitis A, B, and C are the most common.
D Hepatitis
Hepatitis E
Inflammation is sometimes caused by an abnormality in one's immune system.
These are different types of autoimmune hepatitis:
Hepatitis with autoimmunity
Cholangitis of the primary bile duct
Sclerosing cholangitis (primary)
Liver Inflammation Symptoms
Adults may experience the following symptoms of liver inflammation:
Initial symptoms may resemble those of the flu.
Yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes (Jaundice)
Pain in the abdomen
Constantly feeling tired and fatigued
Feelings of nausea or vomiting
Vomiting blood
Abdominal enlargement
Vomit that resembles coffee powder in color
Joint discomfort
Loss of appetite
The urine's dark color
Stool with a lighter color than usual
If you are experiencing any or all of the above-mentioned signs of liver inflammation, please consult your doctor as soon as possible as this could be the case of an inflamed liver.
What factors contribute to liver inflammation?
The liver can become inflamed for a variety of reasons. Some of the possible causes of an inflamed liver include:
Alcoholic cirrhosis, also known as fatty liver disease
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Certain autoimmune disorders
The flow of blood to the liver is reduced.
Tylenol and statins are two examples of heart supplements.
Iron overload in the body (Hemochromatosis)
Fatty liver disease that is not caused by alcohol
The obstructive type of jaundice
Virus infections of various types
Excessive copper buildup in the body (Wilson's disease)
How is Liver Inflammation identified?
The doctor will recommend a series of blood tests to determine the nature of the inflammation. This is done to determine the current enzyme level or even the virus type present. Various imaging techniques, such as CT scans, MRI scans, and ultrasound, aid in gaining a better understanding of the liver.
Magnetic Resonance Elastography is a test used to determine the level of stiffness in the liver. Finally, in some cases, the doctor may perform a liver biopsy to send for further testing.
What are the risks associated with Liver Inflammation?
The complications of liver inflammation differ depending on the cause. If left untreated, it can lead to liver failure, a serious medical condition.
What is the treatment for liver inflammation?
The treatment of an inflamed liver is determined by the underlying cause. In the case of a fatty liver, the patient is advised to lose weight, limit alcohol consumption, and take Vitamin E supplements.
Eat a variety of fresh foods, avoid processed foods, and consume plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables. Dietary calories should be distributed as follows: 40% to 50% of calories should come from carbohydrates, 30% from fat, and 20% to 30% from protein.
The doctor may advise surgery to remove any benign cysts found in the liver. In severe cases of liver inflammation, the doctor may consider the patient as a candidate for a liver transplant.
Depending on the symptoms, the doctor will prescribe medication to treat liver inflammation. In general, there is no medical treatment for an inflamed liver. Chronic hepatitis B can be treated with an antiviral medication in addition to interferon alfa. Antivirals, ribavirin, or ribavirin in combination with interferon alfa may be used to treat chronic hepatitis C. Corticosteroids can be used to treat autoimmune hepatitis.
What steps can be taken to avoid liver inflammation?
Some of the steps that can be taken to prevent liver inflammation include:
Maintain a healthy body weight by exercising regularly and eating a nutritious diet.
Consumption of alcohol in moderation
Avoid coming into contact with other people's bodily fluids.
Use caution when engaging in sexual activity.
Do not consume any contaminated food products.
When using toxic chemicals and insecticides, protect your skin.
Obtain the Hepatitis A and B vaccines.
What is it like to live with Liver Inflammation?
If treated properly and on time, liver inflammation is not a life-threatening disease. If untreated, it can lead to serious medical problems such as acute liver failure. Many people all over the world suffer from liver inflammation disease. This is primarily due to a sedentary lifestyle. Certain dietary changes, regular exercise, healthy food swaps, alcohol control, medication monitoring, and regular doctor visits can all help to manage the condition effectively.

0 comments